
What is UWB?
Like Bluetooth and Wi-Fi, ultra-wideband (UWB) is a short-range, wireless communication protocol that operates through radio waves. But unlike its counterparts, it operates at very high frequencies — a broad spectrum of GHz frequencies — and can be used to capture highly accurate spatial and directional data. Think of UWB as a continuously scanning radar that can precisely lock onto an object, discover its location and communicate with it.
With its fine precision, fast transmission and high reliability, UWB technology is poised to help companies locate people and objects moving in all sorts of environments and processes.
One highly relevant use case in today’s workforce is social distancing. As organizations return to the workplace safely and securely, they also still need to consider physical distancing guidelines. With UWB technology, a wearable sensor could alert an employee when they get too close to someone.
For any organization involved in manufacturing, UWB could be an essential part of digitizing production and logistics. Now, people and items don’t need to be stationary to be recorded; they can also be mobile. UWB could help seamlessly digitize warehouses, shop floors and process chains, stabilizing internal processes and optimizing productivity.
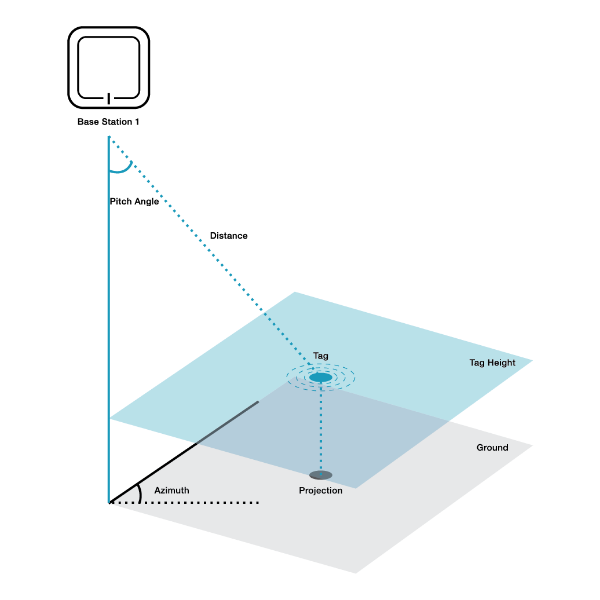
Our UWB Positioning System is determined by the algorithm measuring the activities in between Base Stations, Tags and the Positioning Engine. The base station and tags should, via UWB signal, achieve very high accuracy of precision of positioning (no obstacles 10-30cm).
UWB Function
- Positioning Principle:
TOA (Time of Arrival), TDOA (Time Difference in Arrival), AOA (Angle of Arrival) - Highly Recognized Radiolocation Technology: Ultra-Wideband (UWB)
- UWB is optimal to locate radio waves as:
A. The pulse width is ultra-narrow (1ns) for timing and positioning, and is naturally resistance to multipath effects
B. It occupies a wide spectrum and is resistant to radio interference at fixed frequencies such as WIFI/Bluetooth
C. Low spectrum power, no interference to radio signals
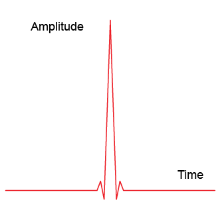
Ultra-Wideband Signals
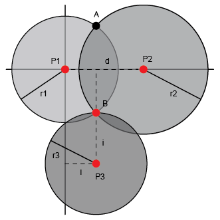
TOA Positioning Diagram
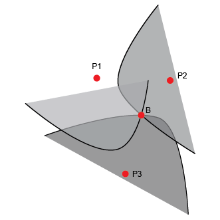
TDOA Positioning Diagram
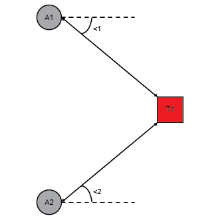
AOA Positioning Diagram
UWB Product Features

Real-time location monitoring
History track replay
Electronic fence management

Flexible label management
Multi-screen convenient viewing
Account permission management

Comprehensive statistics

Autonomous phone positioning

Open API

Camera linkage

Big data analytics
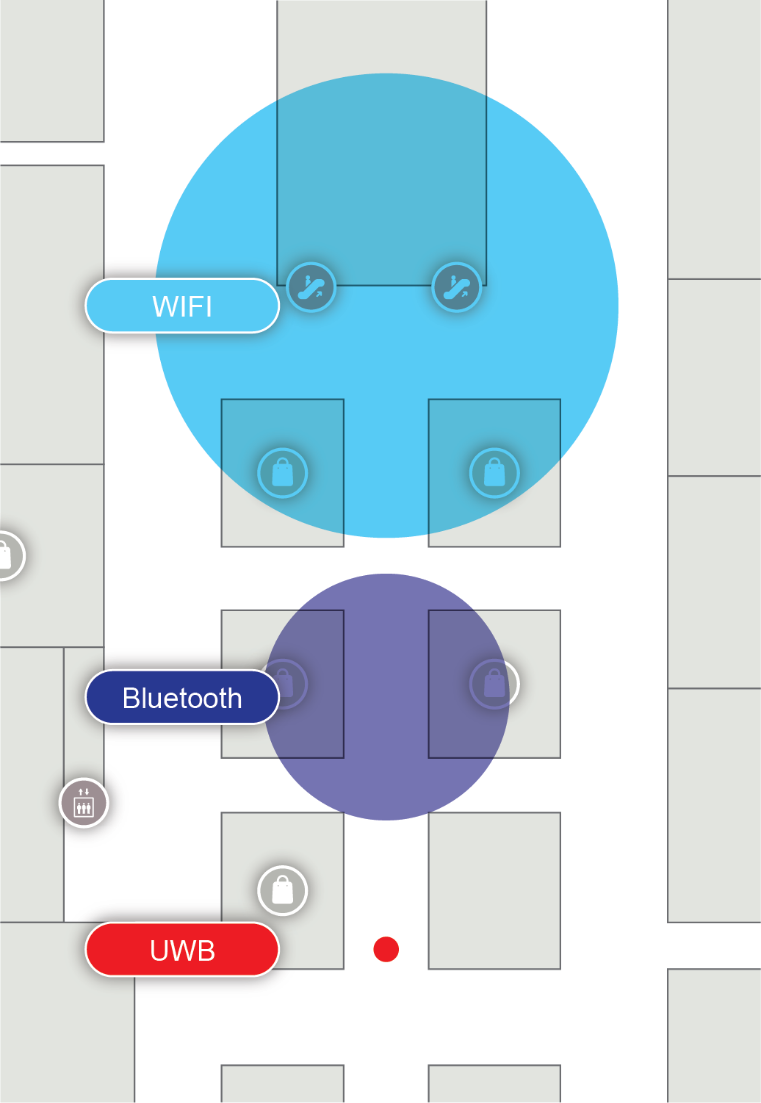
Technologies Comparison
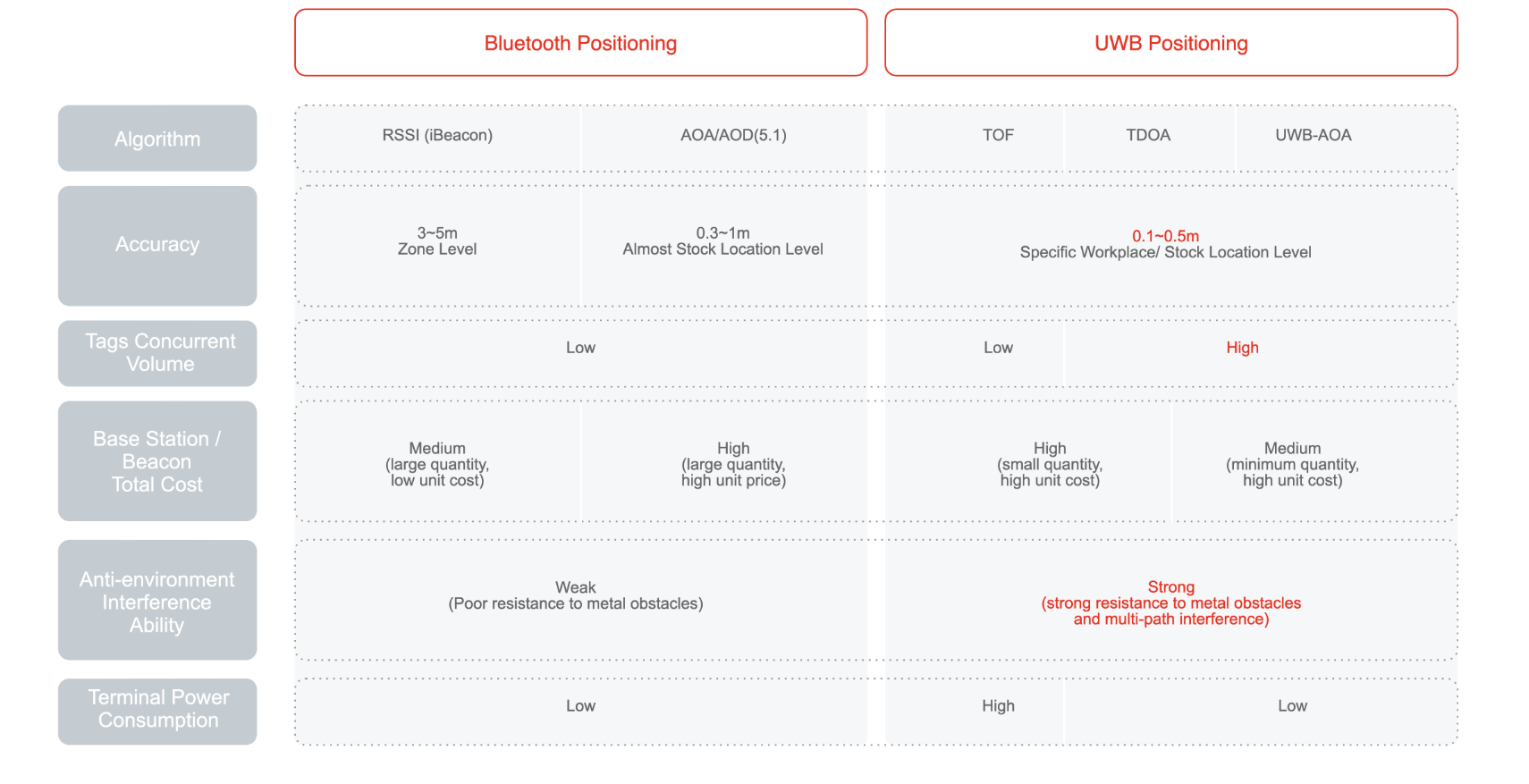
WIFI
| Parameters | 5-10m |
|---|---|
| Feature | Advantages:
Disadvantages:
|
| Deployment | AutoNavi Program Parameters: Deployed at intervals of 30m, 1 AP of 700 is hundreds of yuan per AP |
Bluetooth
| Parameters | 3-5m |
|---|---|
| Feature | Advantages:
Disadvantages:
|
| Deployment | AutoNavi Program Parameters: Deployed at internals of 8 meters, 1 beacon of 50 for 10 yuan each |
Our Product
| Parameters | 10-30m |
|---|---|
| Feature |
|
| Deployment | Open Area Base stations can be deployed 100m apart |
Positioning accuracy comparison
System Architecture
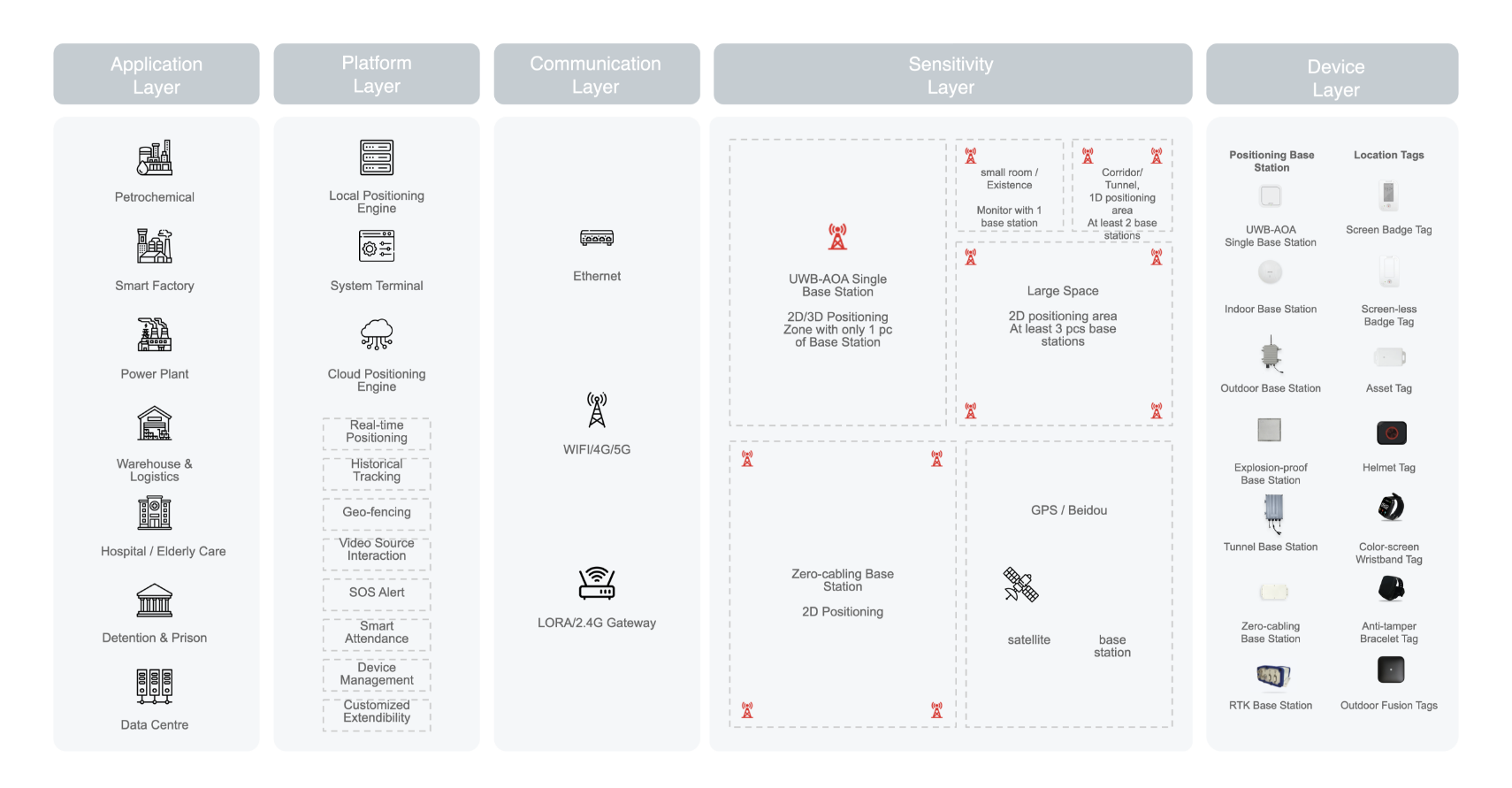
Achievement
The UbiTraq UWB products, that we are authorized to resell are state-of-the-art in the world and so-called using the the top-tier grade of UWB technologies. The achievement, not limited to, covers the below:
UWB-AOA product – “2022 Chain IoT Industry Innovative Product Rank”
2022 – The Top-50 China IOT Enterprise with high valuation to be invested
2022 IOTE Innovative Product Gold Award
Landmarking projects: 3-1 Smart Manufactory, Tencent Data Centre, JD Smart Warehouse, CUHK Hospital, Beijing Winter Olympics Speed Skating Oval
Transportation projects: National airports, Beijing Metro, Shenzhen Metro

Example of UWB Process
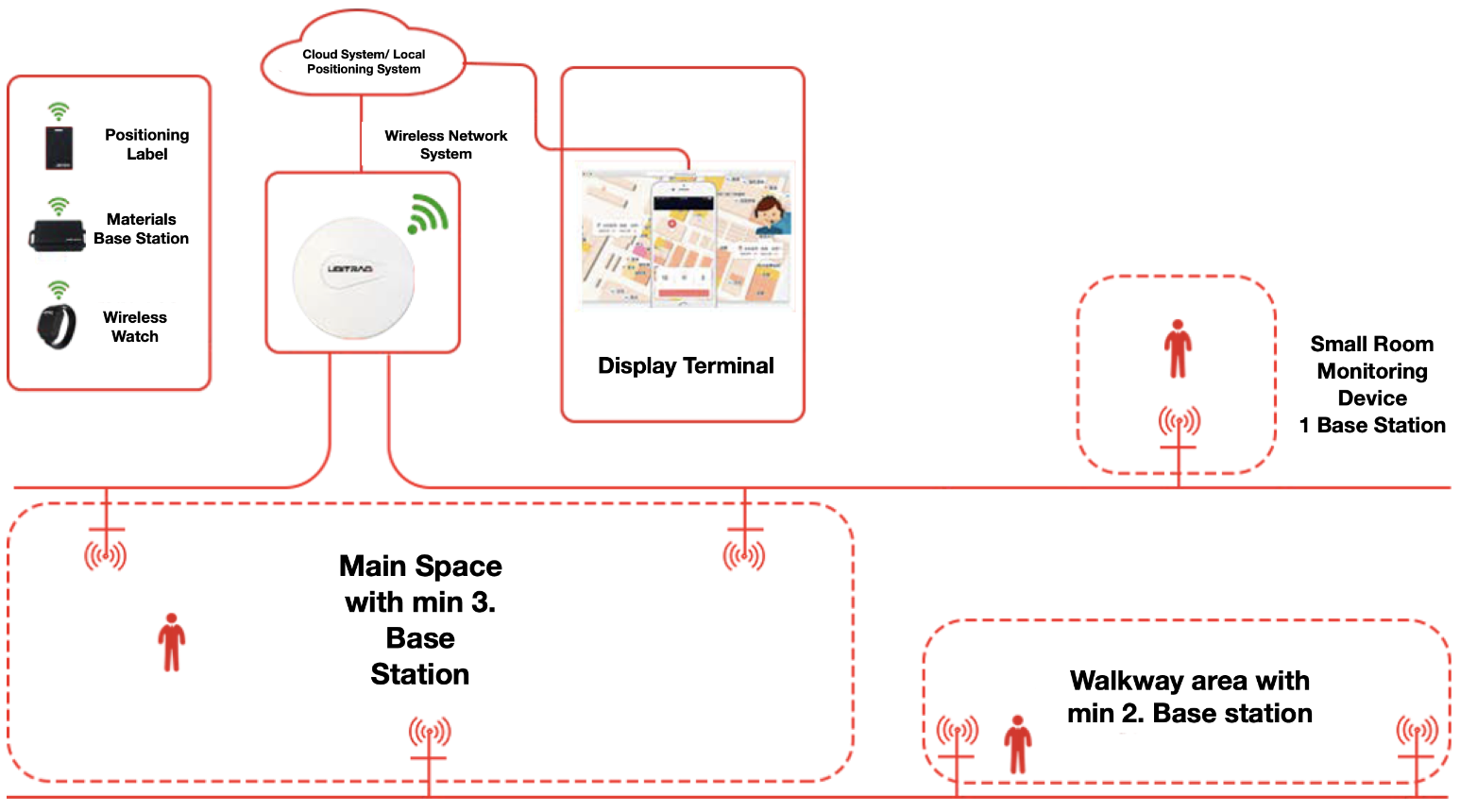
Base Station
Usage of UWB Technology to position a space indoors.
Required to be installed in the space in advance.
Base Station will communicate via a USB signal and a positioning tag
Implement the positioning function of labels
Label
Personnel must wear the label in order to be located
Tag will emit a UWB signals with the base station, giving it an exact location
Engine Positioning
Base Stations in the environment are sent to the location engines in real time via the network raw data, which may be located on an on-premises server or in the cloud. The engine positioning position the algorithm and calculates the coordinates position of the label in the real time.
Display Terminal
The label coordinates are calculated by the positioning engine are rendered on the display terminal. The terminal may be any screen with a browser such as a tablet or any display device
Industry Solutions
QBS is a leading provider of cutting-edge IoT solutions and services, catering to diverse industries worldwide. With a deep understanding of our clients’ unique challenges, we specialize in delivering customized applications that leverage IoT devices and platforms, seamlessly integrated with our hardware solutions.
At QBS, we pride ourselves on our ability to analyse and comprehend our clients’ specific needs. Through this process, we gain valuable insights into their pain points and requirements, enabling us to develop tailored IoT applications that address their precise challenges.
Our team of experts combines technical expertise with industry knowledge to design and implement IoT solutions that empower our clients to achieve their business objectives. We offer a comprehensive range of services, from IoT device selection and integration to platform development and deployment.
By harnessing the power of IoT, our clients benefit from enhanced operational efficiency, improved productivity, and increased revenue opportunities. Whether it’s optimizing processes, enabling real-time data analysis, or driving innovation, our IoT solutions are designed to unlock the full potential of connected devices and networks.
With a global reach and a proven track record of success, QBS has established itself as a trusted partner in the IoT landscape. We collaborate closely with our clients, acting as a strategic advisor and providing end-to-end support throughout the project lifecycle.
Experience the transformational power of IoT with QBS. Let us help you navigate the complexities of IoT implementation, harness the capabilities of connected devices, and unlock new opportunities for growth and success. Contact us today to learn more about our world-class IoT solutions and services tailored to your industry and specific requirements. Together, we can drive innovation and shape a connected future.
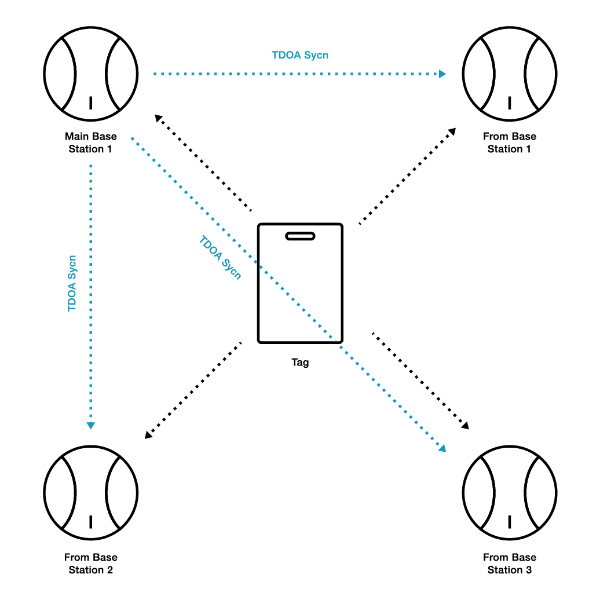
TDOA Positioning Principle
Through the utilization of Ultra Wide Band (UWB) technology, the time difference between the tag and different base stations is leveraged to enable the transmission and reception of UWB signals. This results in the creation of multiple hyperbolas based on the time differences, and the intersecting area of these hyperbolas accurately determines the position of the tag. In the uplink TDOA mode, the tag periodically sends TDOA uplink/downlink broadcast UWB signals to the base station, while in the downlink TDOA mode, the tag receives UWB signals from the base station. It is crucial for the base stations to undergo high precision synchronization with each other, with UWB signals serving as the mainstream method for wireless time synchronization. This precise synchronization allows for accurate positioning and robust performance in UWB-based systems.
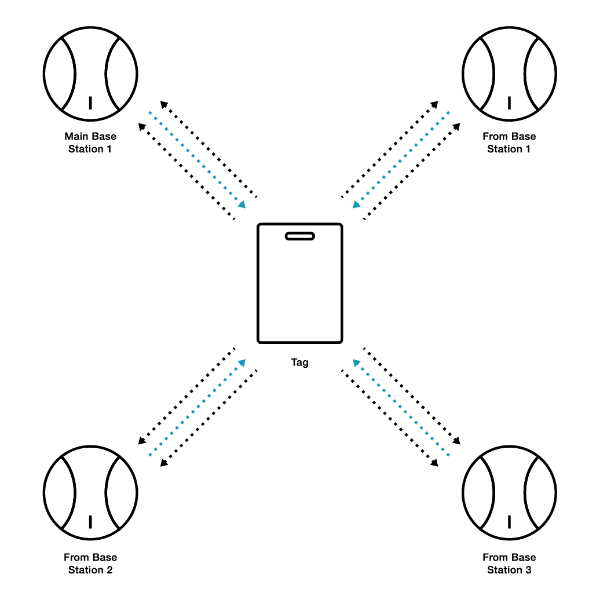
TOF Positioning Principle
In the TWR (Two-Way Ranging) algorithm, a visual representation can be illustrated with the base station as the centre. Spheres are drawn with the distance between the tag and the base station as the radius, signifying the possible locations of the tag. The distance between the tag and the base station is determined through multiple measurements of sending and receiving pulse signals. By calculating the time of flight and utilizing precise timing synchronization, the TWR algorithm enables accurate distance estimation between the tag and the base station. The intersecting area among these spheres represents the actual position of the tag, allowing for precise localization in UWB-based systems.
UWB-AOA Positioning Principle
Phased array radar technology serves as a reference for achieving accurate positioning in UWB-based systems. By utilizing angle measurement and distance measurement techniques, a single base station can achieve precise localization. The inner cover UWB antenna array plays a crucial role by leveraging PDOA (Phase Difference of Arrival) to determine the signal stereo angle and TOF (Time of Flight) to measure the distance to the tag. This combination of angle and distance measurements enables accurate positioning of the tag in three-dimensional space. With an effective coverage radius exceeding 20 meters and exceptional accuracy, this approach outperforms traditional schemes. The capability of a single base station to locate the tag’s 3D position showcases the advanced capabilities of UWB technology in achieving reliable and precise localization.
UWB Base Station

| Model | UT100-AM |
|---|---|
| Positioning Technology | UWB-AOA |
| Size | 180(L)*180(W)*49(H)mm |
| Weight | 530g |
| Coverage | Area: 1000 Effective Radius >20m |
| Positioning Accuracy | 10-30cm |
| Operating Temperature | -30 to 70 |
| Storage Temperature | -40 to 80 |
| Protection Level | IP67 (Sealed and waterproof) |
 Precision Positioning
Precision Positioning Large Coverage
Large Coverage Adaptable to Complex Environment
Adaptable to Complex Environment Low Implementation Cost
Low Implementation Cost Patented Technology
Patented Technology HUWB/FiRa
HUWB/FiRa UWB-AOA single base station has passed the authoritative test of China Academy of Information and Communications Technology China Telecommunication Technology Labs
UWB-AOA single base station has passed the authoritative test of China Academy of Information and Communications Technology China Telecommunication Technology LabsUWB Tags
Application

Warehouse
- Accurate asset tracking
- Vehicle dispatchment
- Efficient operation management
- Streamlined order fulfillment
- Data-driven insights
Power Plant
- Real time tracking of restrict assess
- Improved safety measures
- Efficient maintenance and inspection

Public Security Bureau
- Precise positioning of personnel in prisons, courts and detection
- Enhanced surveillance
- Crowd management
- Collaborative operations

Hospital
- Patient and staff tracking
- Infection Control
- Accurate positioning
- Increase emergency response

Mining
- Real time location tracking of personnel and equipment
- Formulate escape routes
- Improved mining planning

Carpark
- Accurate vehicle tracking
- Improved space utilization
- Efficient traffic flow
- Contactless payment and ticketing








